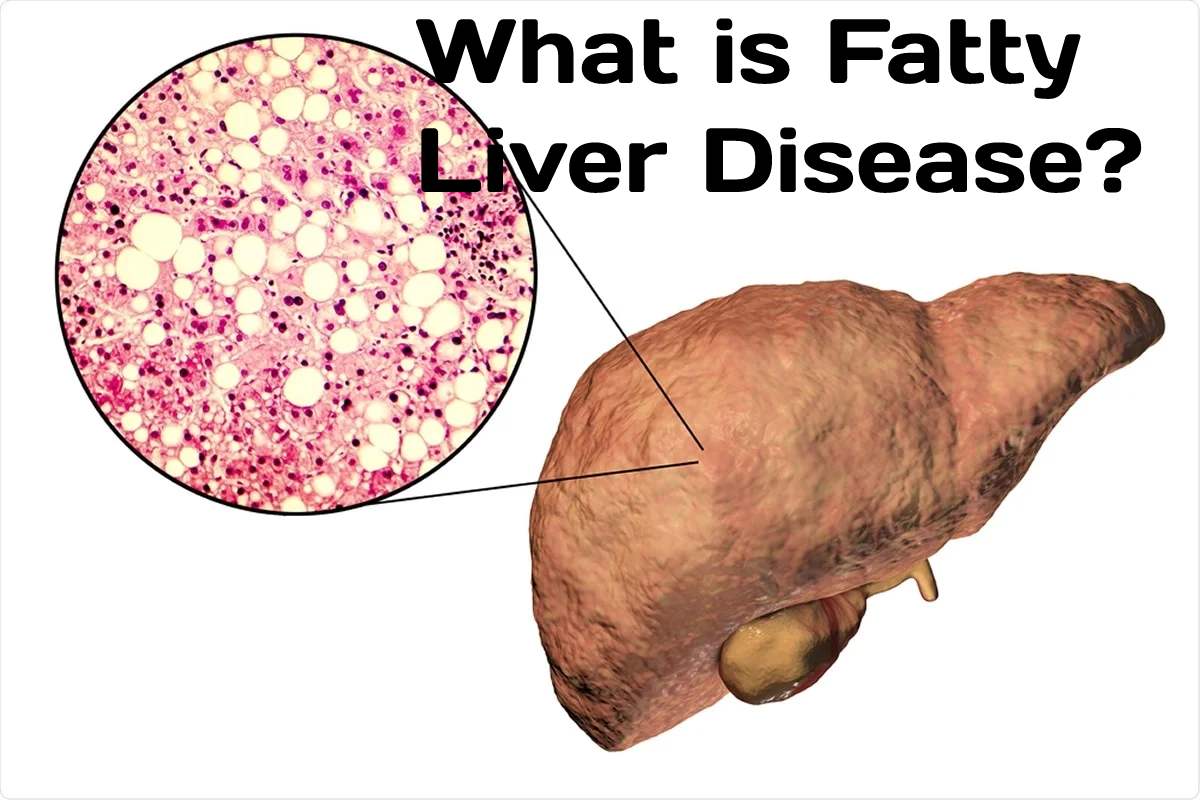
Fatty liver disease is an illness in which fat builds up in the liver. The liver is the main organ within the body. It helps digest food, store energy, and eliminate toxins. There are two main types:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease is also identify as alcoholic hepatic steatosis.
Table of Contents
What is non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a kind of fatty liver that is not related to alcohol consumption. There are two types:
Simple fatty liver: The liver contains fat but little or no inflammation or damage to the liver cells. Simple fatty liver is not severe enough to cause liver damage or complications.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Inflammation and damage to cells and fat in the liver. Inflammation and damage to liver cells can cause liver fibrosis or scarring. Steatosis can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.

What is Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
As its name implies, alcoholic fatty liver disease begins with excessive alcohol consumption. Your liver breaks down the alcohol you drink so it can remove from your body, but the breakdown process can produce harmful substances. These substances can damage liver cells, cause inflammation and weaken the body’s natural defences. The more alcohol you drink, the more your liver hurts. Alcoholic fatty liver disease is the early stage of alcoholic liver disease (or alcoholic liver disease). The following stages are alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
What Causes Fatty Liver Disease?
Several factors can cause or contribute to the development of fatty liver:
Obesity: Obesity, in general, causes low-grade inflammation that can promote the accumulation of fat in the liver. It means that 30% and 90% of overweight adults have NAFLD, and the condition is increasing in children due to the obesity epidemic.
Excess abdominal fat: People of average weight can have fatty liver if they have “visceral obesity”; This means they have a lot of fat around the waist.
Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance and high insulin levels increase the accumulation of fat in the liver in persons with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
High consumption of refined carbohydrates: Frequent consumption of refined carbohydrates promotes the accumulation of fat in the liver, especially when consumed in large amounts by overweight people or resistant to insulin.
Consumption of sugary drinks: Sugary drinks such as sodas and energy drinks are high in fructose, which causes fat to accrue in the liver in children and adults.
Poor gut health: Recent research suggests that an imbalance in gut bacteria, intestinal barrier function (“leaky gut”), or another health problem in this area may contribute to NAFLD.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
There are some signs and symptoms of fatty liver, but not all of them may be present.
You may not even see you have the condition.
- Fatigue and weakness
- Mild pain or feeling of fullness in the right or central abdominal area
- Elevated levels of liver enzymes, including AST and ALT
- Increased insulin levels
- Increased triglyceride levels
If fatty liver progresses to NASH, the following symptoms may occur:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Moderate to severe abdominal pain
- Yellow eyes and skin
It will help if you visit your doctor regularly for routine check-ups and blood tests, which can diagnose fatty liver at an early and reversible stage.
Supplements that can help Fatty Liver
Several research findings suggest that specific vitamins, herbs, and other supplements may help reduce liver fat and the risk of developing liver disease.
However, in most cases, experts say more studies are needed to confirm this.
Also, talking to your doctor before taking any supplements is essential, especially if you take medications.
Milk thistle
Milk thistle, or silymarin, is an herb known for its liver-protective effects.
Some studies have found that milk thistle, combined with vitamin E, may help reduce insulin resistance, inflammation, and liver damage in people with NAFLD.
Berberine
Berberine is a plant compound that significantly lowers blood sugar, insulin, and cholesterol levels, among other health markers. Several studies also suggest that it may benefit people with fatty liver.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Many health benefits have been attributed to omega-3 fatty acids. The long-chain omega-3s EPA and DHA start in fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel. Therefore several studies show that omega-3 can improve liver health in adults and children with fatty liver.
Conclusion
Fatty liver can lead to various health problems. Fortunately, it can reverse if caught early. Following a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and perhaps taking supplements can reduce excess fat in the liver and lower the risk of progression to more severe liver disease.
Also Read: Lynch Disease – Symptoms, Diagnosis, and More